Metric Re-definition by Leadership: Top leadership periodically redefines S&G metrics to ensure relevance and alignment with business and regulatory needs.
Survey Distribution by Team Managers: Team leaders distribute surveys based on these metrics, where participants rate risks using a 3x3 risk matrix to evaluate likelihood and severity.
Data Compilation and Self-Assessment: Team leaders consolidate survey data, creating visualizations to assess project compliance with S&G standards.
Benchmarking and Self-Reflection: Teams use these visualizations to benchmark performance, stimulating innovative ideas for better alignment with S&G metrics in future projects.
Information Loop to Leadership: Insights from self-assessment and benchmarking are communicated to top leadership, fostering continuous improvement and an innovation culture across the risk division.
Reflecting on our progressive improvement plan, I see how integral continuous enhancement is to our success. By actively participating in this process, I feel empowered to contribute to refining our internal processes and ensuring they align with our organizational goals. This approach allows us to address policy and social issues gradually, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Incorporating the Project Self-assessment and the three lines of defense risk management principles into our corporate structure has made me feel more secure in our risk prevention and control measures. This integration is not only stabilizing our operations but also enhancing our leadership development. I anticipate that our compliance with external audits will improve significantly, and the N+1 level management model will enable us to respond quickly to risk breakdowns, clarifying responsibilities and streamlining processes.
This robust defense mechanism reassures me that policy-related issues will be minimized, and my sense of identification with the company has grown. I feel a heightened sense of responsibility and engagement, knowing that my contributions can indirectly manage and improve the business.
As this innovative culture becomes more ingrained in our daily operations, I am excited about the possibilities and creativity it will unlock for Macquarie Group. This reflection highlights how our active participation and commitment to continuous improvement are driving our organizational success.
The SG-Rose reflects Macquarie Group's dedication to key Social and Governance (S&G) attributes, fostering an innovation culture beyond mere compliance. It makes risks and performance visually comprehensible, promoting proactive problem-solving and positioning Macquarie as a leader in responsible financial services.


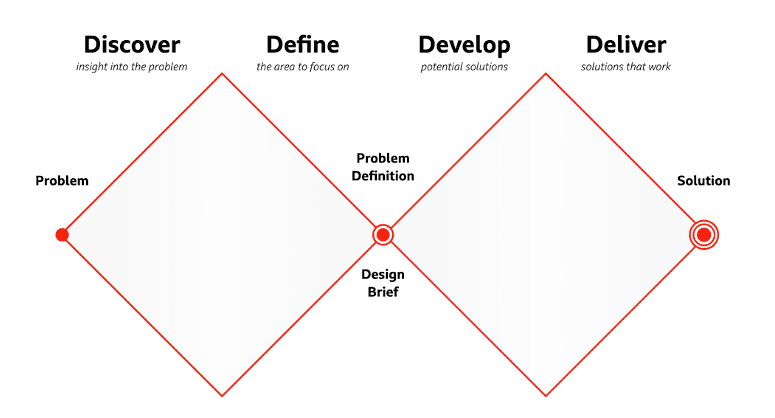
The final phase involved refining the SG-Rose model based on user testing feedback. Participants engaged with the prototype, providing insights that were instrumental in fine-tuning the system, ensuring its functionality and alignment with user expectations.
The refined ideas were then converted into tangible prototypes. A visual map intertwining Doughnut Economics with focused Social and Governance metrics from ESG principles was drawn. This matrix serves as a tool for Macquarie to balance employee welfare and robust governance. The prototype used dots to represent employee feedback, with green indicating alignment with company standards and red highlighting areas needing attention.
With a clearer direction, the ideas were subjected to external feedback during in-class tutorial sessions. This led to the suggestion of a Social and Governance measurement tool, which the team decided to adapt using the doughnut economics framework. Visual sketches of the measurement tool were created to enhance its validity and reliability.
The design journey began with a creative burst, facilitated by KJ Brainstorming. This collaborative method helped gather, categorize, and reflect on diverse ideas, leading to the conceptualization of an engaging ESG dashboard for the risk division. Other ideas included a Social and Governance collaborative workshop and community engagement platforms, showcasing the team's broad creativity.
User Testing
Low-Fidelity Prototype
Iteration
Initial Conceptualization
Reflection
Workflow
Design Offering
Design Process
Key Insights
Secondary Research

The Importance of ESG Principles: Integrating ESG (environmental, social, and governance) criteria is crucial for enterprises to manage governance risks and social inequality. These principles help assess an enterprise's impact, drawing attention from investors and consumers.
Innovation and Risk Management: Focusing on social and governance elements aids in identifying and mitigating various risks, such as regulatory changes, supply chain disruptions, and reputational damage. This risk awareness can drive innovation in internal architecture, business processes, and market strategies.
ESG-Driven Competitive Advantage: Operating within an ESG framework offers competitive benefits, including attracting conscious consumers and investors, enhancing reputation and brand image, attracting top talent, reducing legal risks, and increasing resilience in a dynamic business environment.
Innovation Risk Management: Establishing processes to manage innovation risks is vital. Companies need to anticipate, avoid, and respond to potential risks effectively.
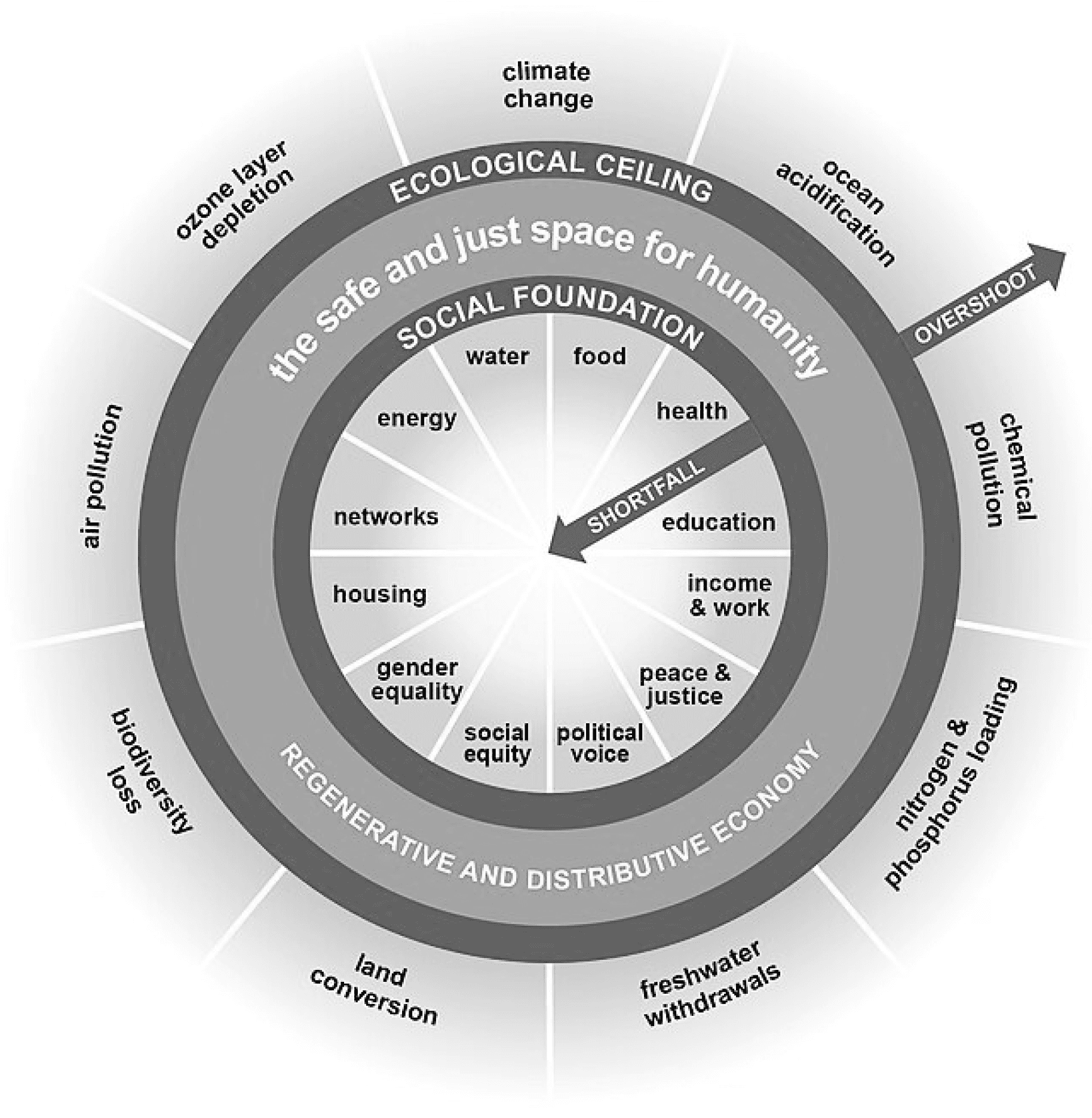
Our research methods, including literature review and interviews, support the idea that ESG drives innovation. We investigated doughnut economics, a framework by Kate Raworth (2017), which advocates for sustainable economic development within safe and just boundaries for humanity, avoiding societal and environmental harm. While still early in business adoption, doughnut economics offers a valuable perspective for assessing social and environmental impacts. We believe this framework aligns well with social and governance principles, presenting an innovative opportunity for Macquarie Group’s sustainable development. This approach can significantly enhance Macquarie's ESG strategies and overall impact.
ESG, standing for environment, society, and governance, is a set of criteria based on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals used to evaluate a company's sustainability practices. As investor and consumer demand for transparency grows, Macquarie Group has identified social and governance risks as more valuable areas for innovation compared to environmental risks.
An ESG innovation culture integrates these principles into the organization’s processes, promoting solutions that address environmental challenges, enhance social well-being, and uphold strong governance. This culture helps companies recognize and integrate ESG factors into their innovation strategies, decision-making, and daily operations.
ESG, standing for environment, society, and governance, is a set of criteria based on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals used to evaluate a company's sustainability practices. As investor and consumer demand for transparency grows, Macquarie Group has identified social and governance risks as more valuable areas for innovation compared to environmental risks.
An ESG innovation culture integrates these principles into the organization’s processes, promoting solutions that address environmental challenges, enhance social well-being, and uphold strong governance. This culture helps companies recognize and integrate ESG factors into their innovation strategies, decision-making, and daily operations.
The project presents an innovative approach to integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles into the corporate fabric of Macquarie Group, advocating for an innovation culture that transcends traditional business practices. At the heart of this transformation is the deployment of a tailored design process, meticulously developed to harness the potential of social and governance dimensions as key drivers for innovation culture. The rationale behind our design process is twofold: to mitigate inherent social and governance risks and to exploit the untapped opportunities within these realms. By drawing inspiration from the holistic "doughnut economics" framework, the report crafts a narrative around the SG-Rose model.
This project-based self-assessment mechanism aligns closely with the principles of doughnut economics. This model embodies a systematic approach to evaluating and enhancing Macquarie Group's ESG performance, underscoring the firm's pledge to innovation, operational excellence, and sustainable progress.
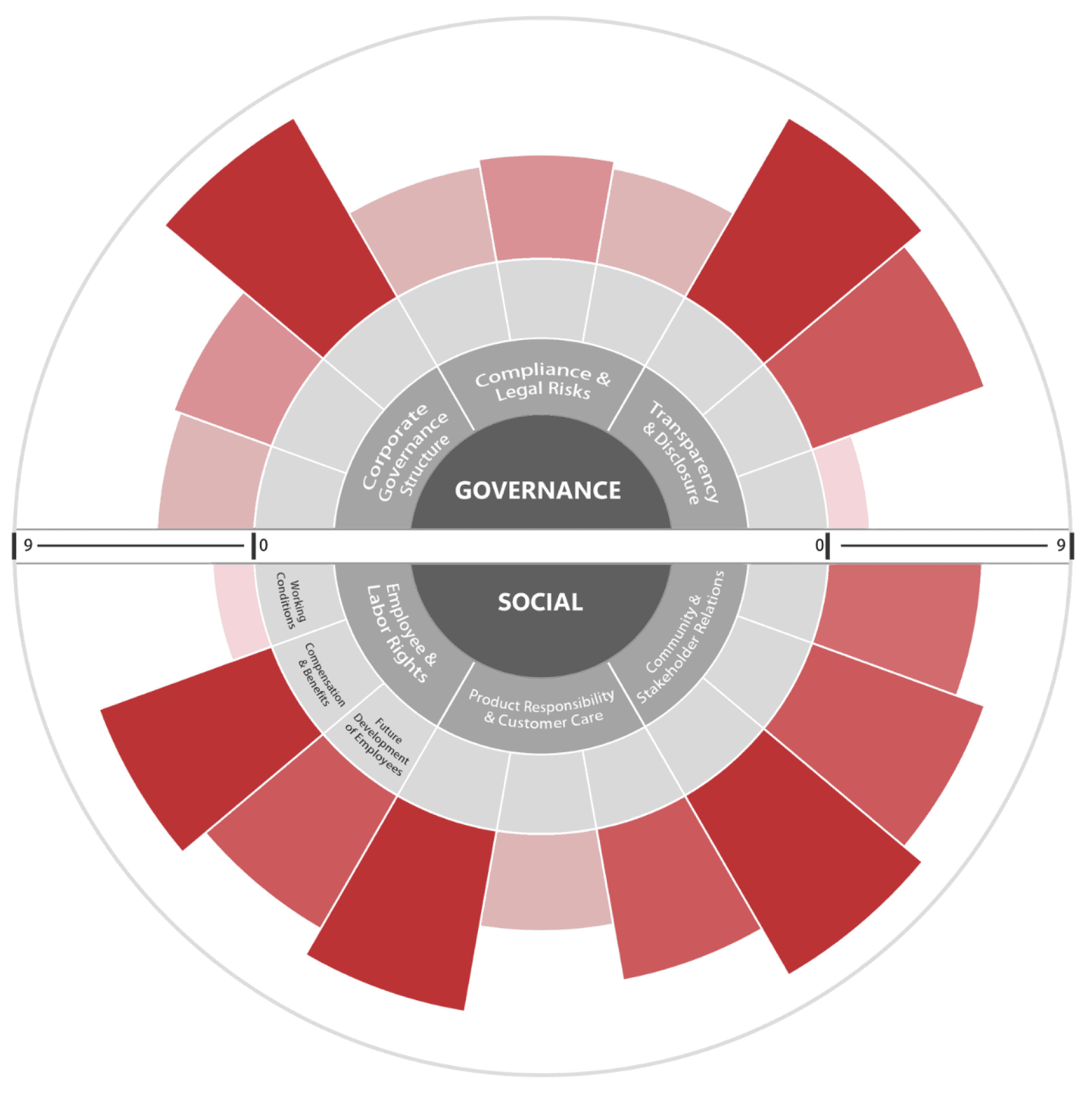
SG-Rose


SG-Rose is an innovative system developed by Macquarie Group to visually represent its alignment with Social (S) and Governance (G) standards. Beyond evaluation, it highlights the company's commitment to these attributes, fostering a culture of innovation and proactive problem-solving, positioning Macquarie at the forefront of responsible financial services.
The SG-Rose operates through a dynamic S&G Project-based Self-assessment Framework, promoting transparency, risk management, and continuous improvement. It aligns with evolving Social and Governance standards and enhances Macquarie's commitment to integrity and stakeholder confidence.